Blog
Dental Implants: Maintenance and Care Protocols
January 26, 2026 / Dentistry

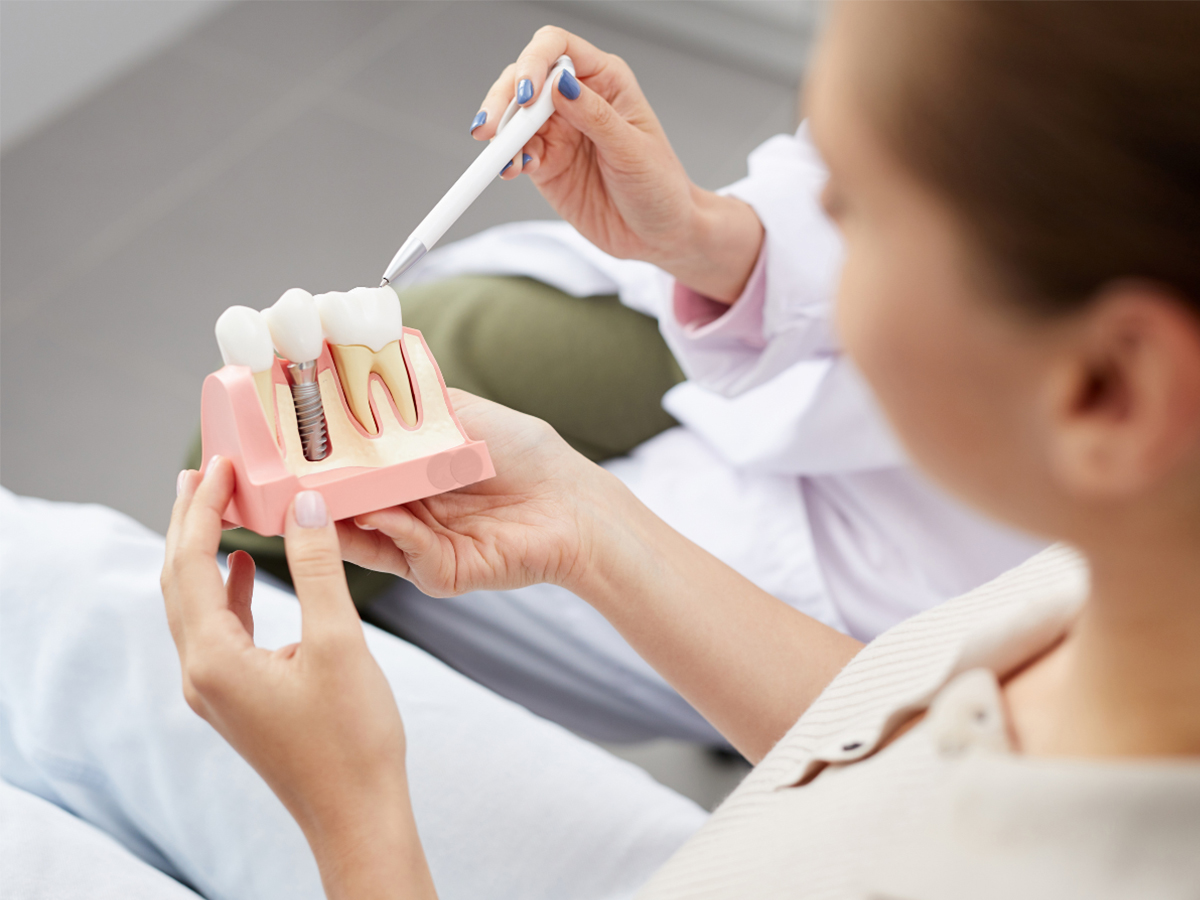
When patients invest in dental implants as a permanent tooth replacement solution, understanding proper maintenance is essential for long-term success. Dental implants require specialized care protocols that differ from natural teeth, involving both professional cleaning techniques and consistent home care routines designed to protect implant health and prevent complications.
At North Toronto Dental Centre, located at 1942 Avenue Rd, North York, ON, M5M 4A1, patients with dental implants receive comprehensive maintenance education and professional care. The dental team recognizes that long-term implant success depends heavily on ongoing maintenance and patient compliance.
Specialized Cleaning Instruments for Dental Implants
Professional maintenance of dental implants requires instruments specifically designed to protect implant surfaces. Traditional metal scalers can scratch titanium implants, creating areas where bacteria can accumulate and increase the risk of complications.
Professional cleaning tools for dental implants include:
- Plastic scalers for gentle plaque removal
- Carbon fiber instruments for calculus removal
- Ultrasonic devices with non-metal tips
- Air polishing systems using glycine powder
- Antimicrobial irrigation solutions
The dental hygienist at North Toronto Dental Centre uses these specialized tools during regular maintenance visits, typically scheduled every three to four months for dental implant patients.
Professional Cleaning Techniques for Dental Implants
Cleaning dental implants requires a gentler yet precise approach compared to natural teeth. Professional maintenance focuses on the implant crown, abutment, and the critical junction where the implant meets the gum tissue.
During each visit, the hygienist evaluates peri-implant tissues for inflammation or infection. Plaque and calculus are carefully removed using implant-safe instruments, followed by antimicrobial irrigation. Polishing is performed using low-abrasive agents specifically formulated for implants to preserve the smooth surface that discourages bacterial buildup.
Peri-Implantitis Prevention Strategies
Peri-implantitis is a serious condition involving inflammation and bone loss around dental implants. Preventing this complication requires proactive care and early intervention.
Key prevention strategies include:
- Professional maintenance every 3–4 months
- Comprehensive plaque control education
- Smoking cessation counseling
- Management of systemic health conditions
- Early detection through regular monitoring
Research shows that patients who maintain consistent professional care have significantly lower rates of peri-implantitis.
Early Detection Through Regular Monitoring
Routine monitoring allows dental professionals to identify early signs of implant-related issues before they progress. Examinations include visual assessments, probing measurements, and radiographic evaluations.
Warning signs may include bleeding on probing, increased pocket depths, discharge, or radiographic bone loss around the implant. At North Toronto Dental Centre, baseline measurements taken after implant placement allow for accurate comparison during future visits.
Patient Education on Proper Flossing Techniques
Home care around dental implants requires specialized flossing methods, as traditional floss may not effectively clean around implant restorations.
Effective flossing aids for dental implants include:
- Super floss for cleaning beneath bridges
- Floss threaders for hard-to-reach areas
- Interdental brushes for wider spaces
- Water flossers for additional plaque control
- Gentle techniques to protect surrounding tissues
Patients receive hands-on instruction during maintenance appointments to ensure proper technique and confidence with these tools.
Brushing Protocols for Dental Implants
Although dental implants cannot develop cavities, the surrounding tissues remain vulnerable to inflammation if plaque accumulates. Proper brushing technique is essential.
Soft-bristled toothbrushes are recommended to prevent tissue trauma, while electric toothbrushes can improve consistency and effectiveness when used gently. Patients should focus on the gum line using small circular motions and spend approximately 30 seconds per implant site to ensure thorough cleaning.
Antimicrobial Rinses and Adjunctive Care
Antimicrobial mouth rinses enhance mechanical cleaning by reaching areas brushes and floss may miss. These rinses help control bacteria around dental implants.
Short-term use of chlorhexidine may be recommended during healing or inflammation, while alternative antimicrobial rinses may be better suited for long-term use. Rinses should always supplement, not replace, brushing and flossing.
Long-Term Success Factors for Dental Implants
Long-term implant success relies on consistent maintenance and healthy lifestyle choices. Studies show implant survival rates exceed 95% over ten years when patients follow recommended care protocols.
Contributing factors include excellent home care, regular professional maintenance, smoking cessation, and management of systemic conditions such as diabetes.
North Toronto Dental Centre offers comprehensive dental implant maintenance services using specialized protocols to protect implant health. Contact the clinic at 416-783-4433 or reception@ntdental.ca to schedule your implant maintenance appointment.
The clinic is open Monday through Thursday from 8:00am to 6:00pm and Friday and Saturday from 8:00am to 3:00pm (two Saturdays per month), providing flexible scheduling for ongoing implant care.
Understanding and following proper maintenance protocols allows dental implant patients to protect their investment and enjoy stable, functional tooth replacement for many years.
Dentist on Avenue Rd: Child-Friendly Pediatric Care
January 10, 2026 / Dentistry

When parents seek quality pediatric dental care, they need a dentist on Avenue Rd who specializes in child-friendly treatment approaches. Children require techniques that differ significantly from adult dental care, with a strong focus on prevention, comfort, and building positive dental experiences that last a lifetime.
At North Toronto Dental Centre, located at 1942 Avenue Rd, North York, ON, M5M 4A1, young patients receive comprehensive pediatric care designed specifically for their developmental needs. The dentist on Avenue Rd team understands that early dental experiences shape lifelong oral health habits.
How Dentist on Avenue Rd Applies Fluoride Varnish
Fluoride varnish application is one of the most effective preventive treatments a dentist on Avenue Rd can provide for children. This simple procedure significantly reduces cavity risk and strengthens developing tooth enamel through remineralization.
The process begins with a gentle cleaning of the tooth surfaces using gauze or a soft toothbrush. The dentist then applies a thin layer of fluoride varnish using a small applicator to ensure complete coverage. The treatment requires minimal cooperation and is typically completed in just a few minutes.
Key benefits of fluoride varnish include:
- Reduces cavities by 33–46% in primary teeth
- Strengthens enamel through remineralization
- Safe for children of all ages, including infants
- Pleasant flavour options for better acceptance
- No rinsing required for 4–6 hours after application
The dentist on Avenue Rd typically applies fluoride varnish every 3–6 months based on cavity risk and individual needs. Children can eat soft foods immediately afterward, making this a convenient option for families.
Sealant Placement for Cavity Prevention
Dental sealants act as protective barriers for permanent molars, helping prevent decay in deep grooves where toothbrush bristles cannot effectively reach. A skilled dentist on Avenue Rd understands the importance of timing, with sealants most effective shortly after molars erupt.
The placement process includes cleaning the tooth, isolating the area, lightly conditioning the enamel, and applying the sealant material, which is hardened with a curing light. Research shows sealants can prevent up to 80% of cavities in treated teeth and last 5–10 years with proper care.
Behavior Management by Dentist on Avenue Rd
Creating a positive dental experience requires a dentist on Avenue Rd to use behavior management techniques rooted in child psychology and developmental understanding. Trust-building and anxiety reduction are key components of pediatric dental success.
The Tell-Show-Do technique is commonly used, allowing children to understand procedures before they occur. This method helps reduce fear and increases cooperation.
Effective behavior management strategies include:
- Positive reinforcement with praise and small rewards
- Calm, confident voice control
- Distraction with music, videos, or conversation
- Gentle physical guidance when necessary
- Nitrous oxide for anxious patients when appropriate
The dentist on Avenue Rd tailors these approaches to each child’s personality, age, and prior dental experiences.
Age-Appropriate Communication Strategies
Clear communication is essential in pediatric dentistry. Younger children respond best to simple explanations and visual demonstrations, while older children benefit from understanding the reasons behind treatments.
For toddlers and preschoolers, the dentist on Avenue Rd avoids frightening language and uses friendly terms while maintaining eye contact at the child’s level. School-age children are encouraged to ask questions and take an active role in their oral health decisions.
Primary Tooth Pulp Therapy
When decay reaches the nerve of a primary tooth, a dentist on Avenue Rd may recommend pulp therapy to preserve the tooth until it naturally falls out. Primary teeth are essential for chewing, speech development, and maintaining space for permanent teeth.
A pulpotomy removes the infected nerve tissue from the crown while preserving healthy tissue in the roots. The tooth is then sealed and protected with a crown, offering pain relief and long-term function.
Space Maintenance for Developing Dentition
Premature loss of primary teeth can lead to alignment issues later. A dentist on Avenue Rd evaluates when space maintainers are necessary to preserve proper spacing for permanent teeth.
Common types of space maintainers include:
- Band and loop for single posterior tooth loss
- Crown and loop for heavily restored teeth
- Distal shoe for early loss of second primary molars
- Lingual arch for multiple missing teeth
These appliances are monitored regularly to ensure they function properly and support normal development.
Preventive Education and Home Care
Education is a core component of pediatric dental care. A dentist on Avenue Rd helps children and parents understand proper brushing techniques, the role of bacteria in cavities, and how daily habits impact oral health.
Dietary counseling also plays a key role, with guidance on limiting sugary snacks, choosing tooth-friendly foods, and encouraging water as the primary beverage between meals.
North Toronto Dental Centre offers comprehensive pediatric dental services using child-friendly techniques and preventive-focused care. Contact the clinic at 416-783-4433 or reception@ntdental.ca to schedule your child’s appointment.
The clinic is open Monday through Thursday from 8:00am to 6:00pm and Friday and Saturday from 8:00am to 3:00pm (two Saturdays per month), offering convenient scheduling for busy families.
Understanding pediatric dental care approaches helps parents prepare their children for positive dental experiences and establish a strong foundation for lifelong oral health.
Archive