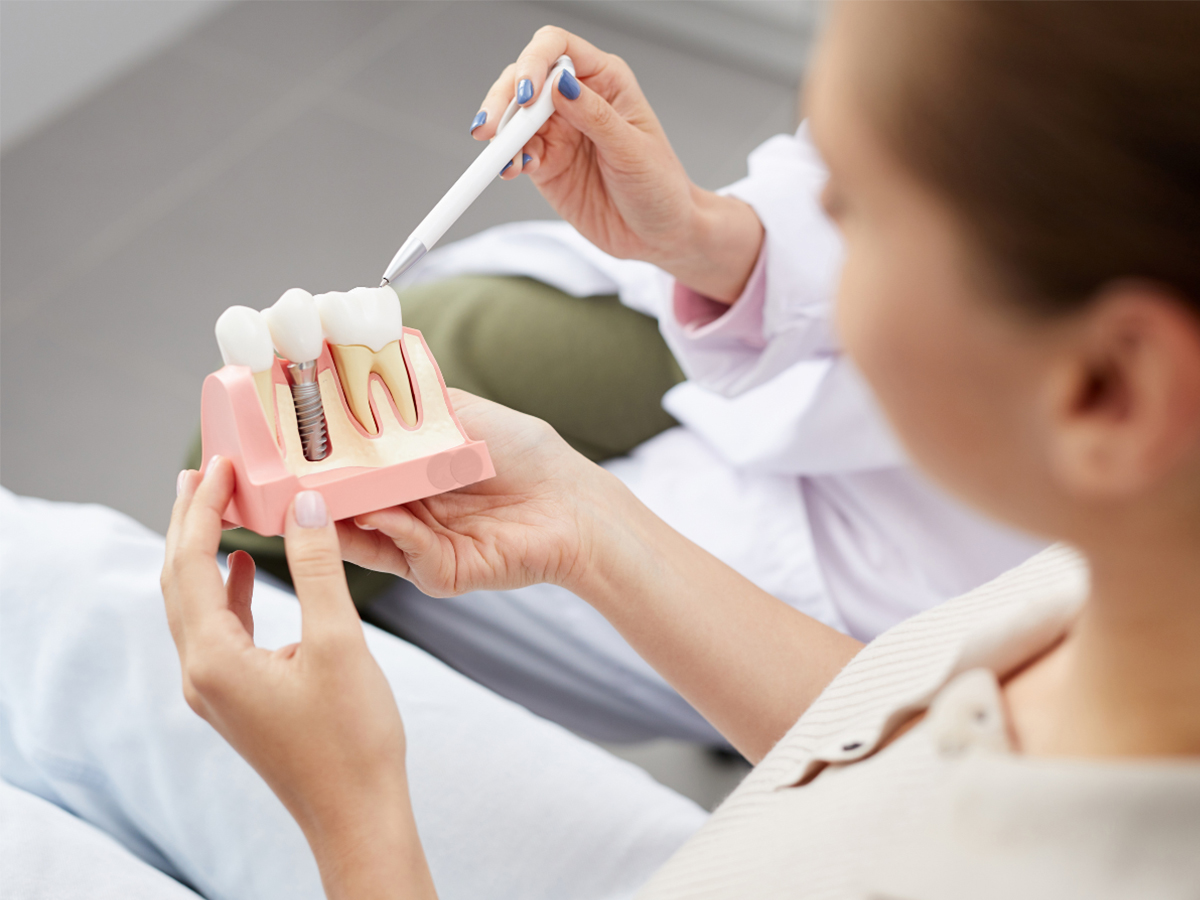
Blog
Invisalign Dentist: Advanced Complex Case Techniques
November 5, 2025 / Dentistry
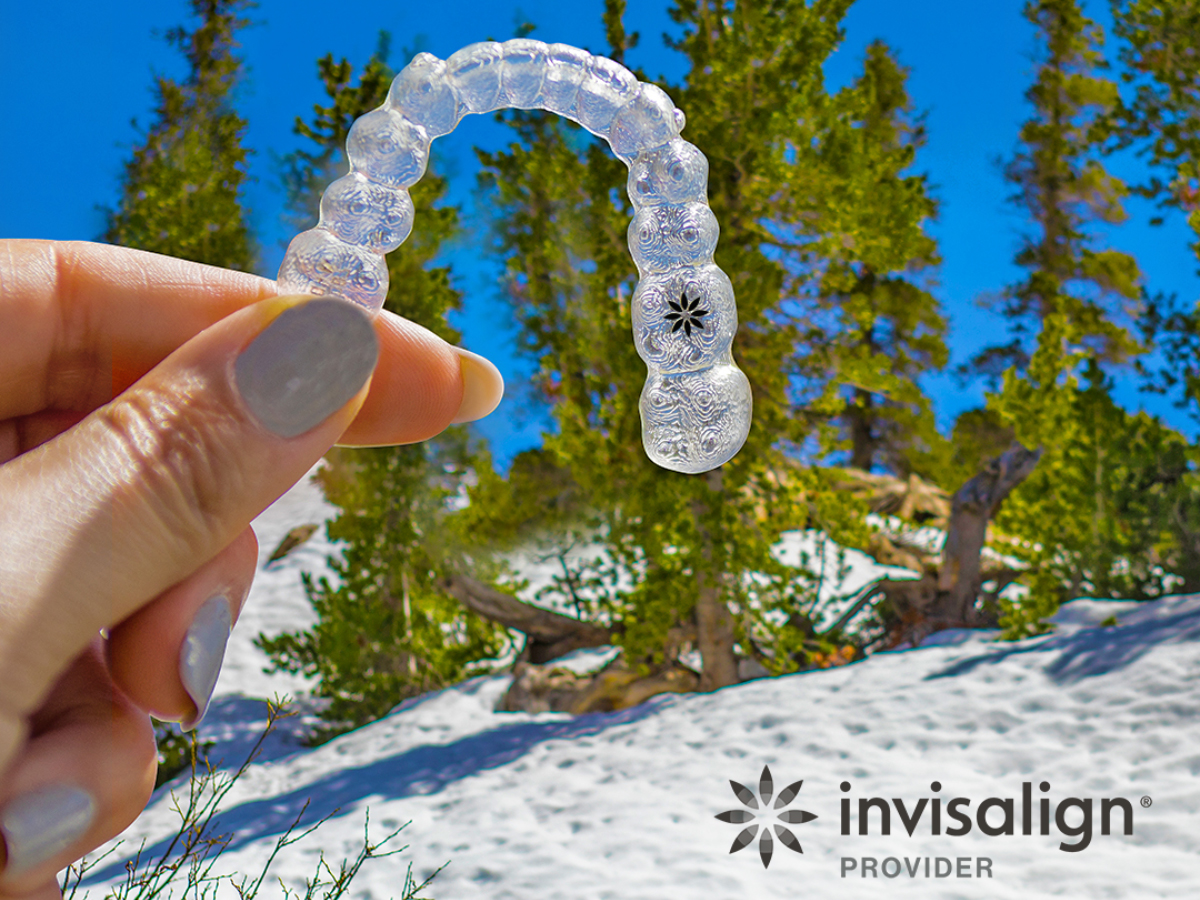

How Invisalign Dentist Corrects Class II Malocclusion
How Invisalign Dentist Corrects Class II Malocclusion
Class II malocclusion presents one of the most challenging cases for an Invisalign dentist. This condition involves the upper jaw positioning too far forward relative to the lower jaw. Traditional treatment required headgear or jaw surgery in severe cases.
Class II Correction Techniques:
- Elastics attached to precision cuts in aligners
- Mandibular advancement through staged aligner design
- Bite ramps built into aligners to encourage jaw repositioning
- Sequential distalization of upper posterior teeth
- Coordinated expansion and advancement protocols
An experienced Invisalign dentist can achieve significant Class II correction using these advanced techniques. Success rates for moderate Class II cases now exceed 85% with proper patient compliance.
Class III Malocclusion Treatment by Invisalign Dentist
Class III Malocclusion Treatment by Invisalign Dentist
Class III malocclusion involves the lower jaw positioning too far forward. This creates an underbite relationship that challenges traditional orthodontic treatment. A skilled Invisalign dentist uses specialized protocols to address this complex condition.
Class III Treatment Approaches:
- Upper arch expansion combined with lower arch constriction
- Proclination of upper incisors using controlled tipping movements
- Retroclination of lower incisors through precise root torque
- Elastics for intermaxillary correction forces
- Staged treatment with refinement aligners
The Invisalign dentist must carefully evaluate growth patterns in younger patients. Adult Class III cases require different approaches compared to growing individuals.
Elastics and Bite Ramps Used by Invisalign Dentist
Elastics and Bite Ramps Used by Invisalign Dentist
Advanced Invisalign treatment relies heavily on auxiliary devices that an Invisalign dentist incorporates into treatment plans. Elastics provide intermaxillary forces that aligners alone cannot achieve. Bite ramps create specific contact points for targeted tooth movement.
Elastic Configurations:
- Class II elastics from upper canines to lower molars
- Class III elastics from lower canines to upper molars
- Vertical elastics for open bite closure
- Cross elastics for midline correction
Bite ramps built into aligners help establish proper vertical relationships. The Invisalign dentist designs these features to guide jaw positioning during treatment.
Severe Crowding Management by Invisalign Dentist
Severe Crowding Management by Invisalign Dentist
Severe crowding cases require an Invisalign dentist to create space through various techniques. Traditional extraction approaches can be avoided in many cases. Modern protocols focus on arch expansion and interproximal reduction.
Space Creation Methods:
- Interproximal reduction (IPR) of 0.2-0.5mm per contact
- Arch expansion using controlled tipping movements
- Molar distalization to create posterior space
- Staged alignment with multiple refinement phases
- Coordinated upper and lower arch development
An experienced Invisalign dentist can resolve crowding up to 6-8mm per arch. This eliminates the need for extractions in most moderate crowding cases.
Interproximal Reduction Protocols
Interproximal Reduction Protocols
Interproximal reduction represents a key technique that an Invisalign dentist uses for space creation. This procedure involves carefully removing small amounts of enamel between teeth. The technique requires precision and expertise to avoid complications.
IPR Guidelines:
- Maximum reduction of 0.5mm per interproximal surface
- Total reduction limited to 50% of enamel thickness
- Staged reduction over multiple appointments
- Immediate fluoride application after reduction
- Careful monitoring for sensitivity or complications
The Invisalign dentist uses specialized strips and discs for precise enamel removal. Digital treatment planning helps determine optimal reduction amounts and locations.
Expansion Protocols by Invisalign Dentist
Expansion Protocols by Invisalign Dentist
Arch expansion allows an Invisalign dentist to create space without extractions. This technique works particularly well in younger patients with developing arches. Adult expansion requires careful evaluation of periodontal support.
Expansion Considerations:
- Gradual expansion of 1-2mm per arch segment
- Monitoring of gingival recession during treatment
- Coordination with vertical dimension changes
- Assessment of TMJ response to expansion
- Long-term stability evaluation
The Invisalign dentist must balance expansion benefits with potential complications. Excessive expansion can lead to relapse or periodontal problems.
Open Bite Closure Techniques
Open Bite Closure Techniques
Open bite correction challenges even experienced Invisalign dentist practitioners. This condition involves lack of contact between upper and lower teeth. Multiple factors contribute to open bite development including tongue habits and skeletal patterns.
Open Bite Treatment Methods:
- Intrusion of posterior teeth using precise force vectors
- Extrusion of anterior teeth through controlled movements
- Bite blocks to break harmful tongue habits
- Vertical elastics for additional closing forces
- Myofunctional therapy coordination
The dentist must address underlying causes while moving teeth. Habit modification becomes crucial for long-term stability. [Literature Review]
Vertical Dimension Considerations
Vertical Dimension Considerations
Managing vertical dimension requires an dentist to understand complex facial relationships. Changes in bite height affect facial support and TMJ function. Careful planning prevents adverse effects on facial aesthetics.
Vertical Dimension Factors:
- Facial height proportions and smile line evaluation
- TMJ function assessment during treatment
- Muscle adaptation to bite changes
- Speech pattern modifications
- Long-term stability of vertical changes
The dentist monitors these factors throughout treatment. Adjustments may be necessary based on patient response and adaptation.
Complex Invisalign Cases at North Toronto Dental Centre
Complex Invisalign Cases at North Toronto Dental Centre
North Toronto Dental Centre provides advanced Invisalign treatment for complex orthodontic cases. Contact them at 416-783-4433 or reception@ntdental.ca to discuss complex case treatment options. The clinic is open Monday through Thursday from 8:00am to 6:00pm. Friday and Saturday hours are 8:00am to 3:00pm (two Saturdays per month). Complex orthodontic cases require an experienced dentist who understands advanced biomechanics. Proper treatment planning and execution can achieve excellent results in challenging situations.
Archive