Blog
Family Dentist: Pregnancy Dental Care Management
December 20, 2025 / Dentistry
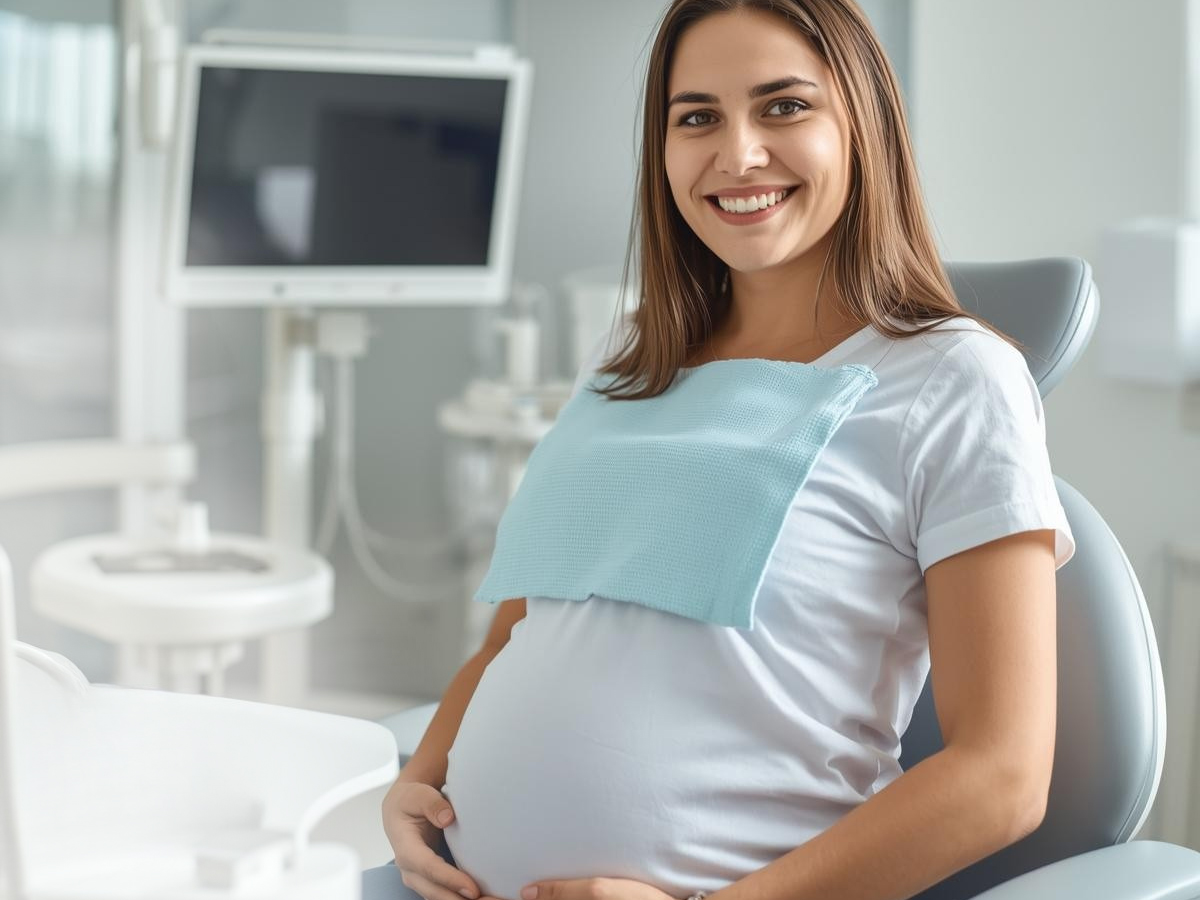

When expecting mothers need dental care, they require a family dentist who understands the unique considerations of pregnancy oral health management. Pregnancy brings significant changes to oral health that require specialized knowledge and careful treatment planning. These changes affect both maternal comfort and fetal safety throughout all stages of pregnancy.
At North Toronto Dental Centre, located at 1942 Avenue Rd, North York, ON, M5M 4A1, pregnant patients receive comprehensive care tailored to their specific needs. The family dentist team understands that maternal oral health directly impacts both mother and baby's wellbeing.
How Family Dentist Manages Trimester-Specific Care
Pregnancy dental care requires a family dentist to understand the unique considerations of each trimester. Different stages of pregnancy present varying risks and treatment opportunities that must be carefully managed.
First Trimester Considerations (Weeks 1-12):
- Organ development period requiring medication caution
- Morning sickness affecting oral hygiene maintenance
- Elective procedures typically postponed
- Emergency treatment provided with careful drug selection
- Folic acid supplementation recommendations
- Dietary counseling for optimal oral health
Second Trimester Considerations (Weeks 13-27):
- Safest period for routine dental procedures
- Optimal time for necessary restorative work
- Pregnancy gingivitis monitoring and management
- Professional cleanings with modified positioning
- Local anesthesia considered safe when needed
Third Trimester Considerations (Weeks 28-40):
- Positioning challenges due to enlarged abdomen
- Shortened appointments to prevent supine hypotensive syndrome
- Emergency care only unless urgent treatment needed
- Preparation for postpartum dental needs
The family dentist adjusts treatment timing and approaches based on these trimester-specific factors while maintaining optimal oral health.
Medication Safety Guidelines by Family Dentist
Medication safety during pregnancy requires a family dentist to understand FDA pregnancy categories and evidence-based prescribing guidelines. Careful drug selection protects both maternal and fetal health.
Safe Medications During Pregnancy:
- Lidocaine (Category B) for local anesthesia
- Acetaminophen (Category B) for pain management
- Penicillin and amoxicillin (Category B) for infections
- Erythromycin (Category B) as penicillin alternative
- Chlorhexidine rinses for antimicrobial therapy
Medications to Avoid:
- Tetracycline antibiotics (tooth staining risk)
- Aspirin in third trimester (bleeding complications)
- Nitrous oxide (limited evidence of safety)
- Benzodiazepines for anxiety management
- NSAIDs in third trimester (premature ductus closure)
The family dentist consults with obstetricians when complex medication decisions arise during pregnancy care.
Pregnancy Gingivitis Management
Pregnancy gingivitis affects up to 75% of pregnant women and requires specialized management by a family dentist. Hormonal changes increase gingival inflammation and bleeding even with good oral hygiene.
Pregnancy Gingivitis Characteristics:
- Increased gingival bleeding during brushing
- Red, swollen, tender gum tissues
- Exaggerated response to plaque accumulation
- Possible pyogenic granuloma development
- Symptoms typically peak in second trimester
Management Strategies:
- Enhanced oral hygiene instruction and motivation
- More frequent professional cleanings (every 3-4 months)
- Antimicrobial mouth rinses when appropriate
- Soft tissue management techniques
- Nutritional counseling for gingival health
The family dentist emphasizes that pregnancy gingivitis is preventable and manageable with proper care and professional monitoring.
Professional Cleaning Frequency Adjustments
Pregnancy requires a family dentist to modify professional cleaning schedules based on individual patient needs and gingival response. Standard six-month intervals may be insufficient during pregnancy.
Recommended Cleaning Schedule:
- First trimester: routine cleaning if due
- Second trimester: ideal time for thorough cleaning
- Third trimester: maintenance cleaning with positioning modifications
- Postpartum: comprehensive evaluation and treatment planning
Cleaning Modifications:
- Shorter appointment durations to prevent fatigue
- Frequent position changes to maintain comfort
- Left lateral positioning to avoid vena cava compression
- Gentle technique with pregnancy-sensitive tissues
- Enhanced post-treatment instructions
The family dentist monitors gingival health closely and adjusts cleaning frequency based on individual patient response and needs.
Radiographic Safety Protocols
Dental radiographs during pregnancy require a family dentist to follow strict safety protocols while obtaining necessary diagnostic information. Modern digital radiography significantly reduces radiation exposure.
Radiation Safety Measures:
- Lead apron with thyroid collar for all exposures
- Digital sensors reducing exposure by 80-90%
- Collimation to minimize radiation field size
- Fastest film speed or digital settings
- Proper technique to avoid retakes
Radiographic Guidelines by Trimester:
- First trimester: emergency situations only
- Second trimester: necessary diagnostic radiographs acceptable
- Third trimester: emergency situations with positioning modifications
- Postpartum: comprehensive radiographic evaluation
The family dentist explains that diagnostic dental radiographs pose minimal risk when proper safety protocols are followed.
Nutritional Counseling for Oral Health
Pregnancy nutrition significantly impacts oral health, requiring a family dentist to provide comprehensive dietary guidance. Proper nutrition supports both maternal oral health and fetal development.
Key Nutritional Recommendations:
- Calcium intake for tooth and bone development
- Vitamin D for calcium absorption
- Vitamin C for gingival health
- Folic acid for tissue development
- Protein for tissue repair and development
Dietary Considerations:
- Frequent small meals to manage morning sickness
- Avoiding sugary snacks between meals
- Rinsing with water after vomiting episodes
- Choosing tooth-friendly snacks and beverages
- Maintaining adequate hydration
Postpartum Dental Care Planning
A family dentist must prepare pregnant patients for postpartum oral health needs and treatment planning. The postpartum period presents opportunities for comprehensive dental care.
Postpartum Considerations:
- Comprehensive oral examination after delivery
- Treatment of conditions postponed during pregnancy
- Breastfeeding medication considerations
- Hormonal changes affecting oral health
- Time management challenges with newborn care
North Toronto Dental Centre provides comprehensive pregnancy dental care with experienced professionals who understand maternal oral health needs. Contact them at 416-783-4433 or contact us to discuss pregnancy dental care options.
The clinic is open Monday through Thursday from 8:00am to 6:00pm, Friday and Saturday from 8:00am to 3:00pm (two Saturdays per month), accommodating the scheduling needs of expectant mothers.
Understanding pregnancy dental care helps expectant mothers maintain optimal oral health while protecting their developing babies through evidence-based treatment approaches.
Emergency Dentist on Avenue Road: Root Canal Crisis
December 5, 2025 / Dentistry
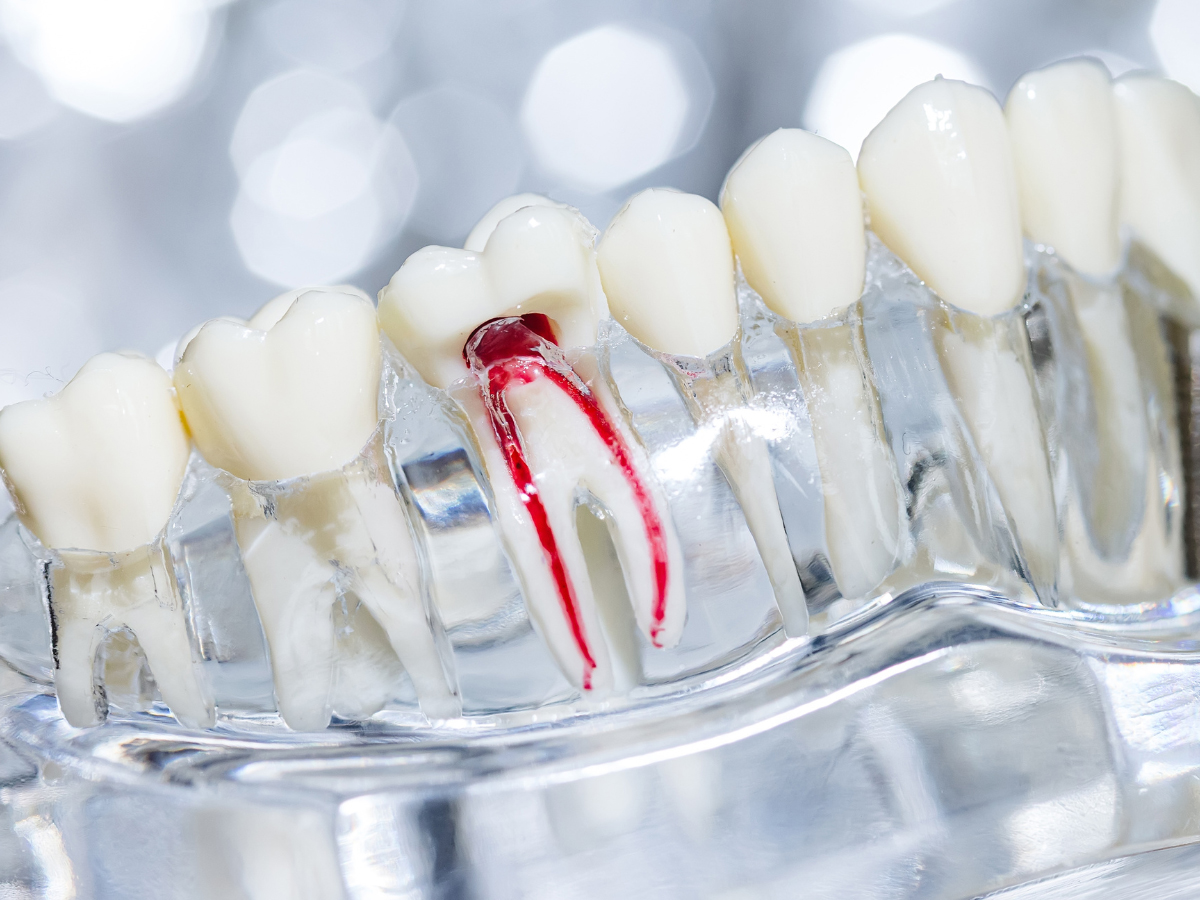
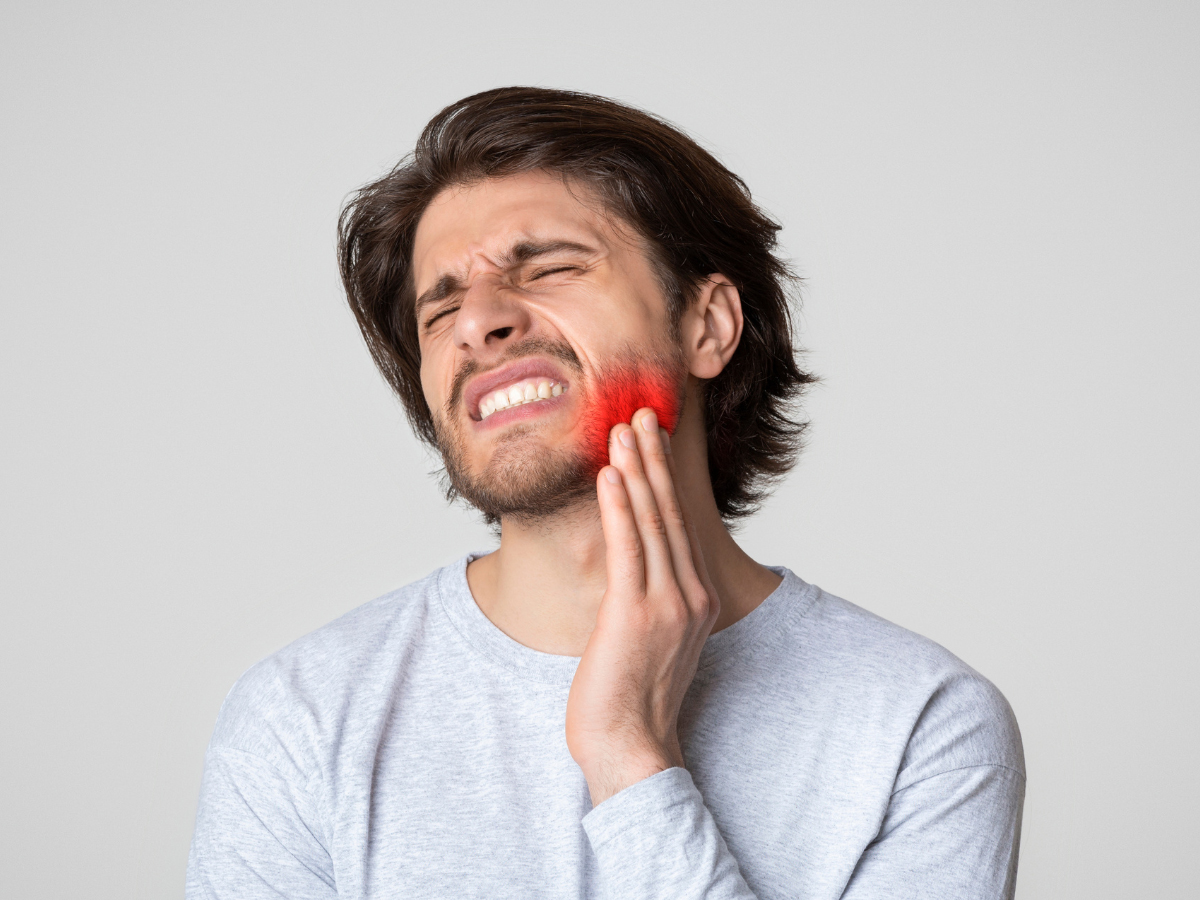
When severe tooth pain strikes suddenly, patients need an emergency dentist on Avenue Road who can diagnose and treat endodontic emergencies effectively. Root canal crises represent some of the most painful dental conditions requiring immediate professional intervention. These emergencies can develop rapidly and cause debilitating pain that disrupts daily life.
At North Toronto Dental Centre, located at 1942 Avenue Rd, North York, ON, M5M 4A1, patients experiencing endodontic emergencies receive prompt, expert care. The emergency dentist on Avenue Road team understands that root canal pain cannot wait for regular business hours.
How Emergency Dentist on Avenue Road Diagnoses Pulpal Necrosis
Pulpal necrosis occurs when the nerve tissue inside a tooth dies due to infection or trauma. An experienced emergency dentist on Avenue Road can identify this condition through clinical examination and diagnostic testing.
Pulpal Necrosis Diagnostic Signs:
- Severe, spontaneous pain or complete absence of pain
- No response to cold testing (negative vitality)
- Possible response to heat in early stages
- Pain with biting pressure (percussion sensitivity)
- Possible swelling or sinus tract formation
- Tooth discoloration in chronic cases
The emergency dentist uses thermal testing and electric pulp testing to assess nerve vitality. Radiographic examination may reveal periapical radiolucencies in established cases.
Immediate Pain Relief Through Emergency Procedures
When patients present with acute pulpal inflammation, an emergency dentist on Avenue Road can provide immediate relief through emergency pulp therapy. This treatment removes infected tissue and eliminates the source of pain.
Emergency Treatment Options:
- Pulpotomy for vital pulp with localized inflammation
- Pulpectomy for non-vital pulp with complete removal
- Access cavity preparation for drainage and pressure relief
- Irrigation with antimicrobial solutions
- Placement of intracanal medicaments
- Temporary restoration placement
The emergency dentist selects appropriate treatment based on pulp vitality testing and clinical presentation. Complete pulp removal is necessary when necrosis is confirmed.
Antibiotic Protocols by Emergency Dentist on Avenue Road
Antibiotics are prescribed by an emergency dentist on Avenue Road when systemic signs of infection are present. These medications supplement, but do not replace, definitive dental treatment.
Antibiotic Indications:
- Facial swelling extending beyond the alveolar process
- Fever above 37.8°C (100°F)
- Malaise or systemic symptoms
- Lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes)
- Trismus (limited mouth opening)
Common Antibiotic Choices:
- Amoxicillin 500mg every 8 hours (first-line choice)
- Clindamycin 300mg every 8 hours (penicillin allergic patients)
- Metronidazole 400mg every 8 hours (anaerobic coverage)
The emergency dentist emphasizes that antibiotics alone cannot cure dental infections without source control through dental treatment.
Managing Acute Apical Periodontitis
Acute apical periodontitis causes severe pain when biting down and requires immediate attention from an emergency dentist on Avenue Road. This condition results from bacterial toxins reaching the tissues around the root tip.
Treatment Approach:
- Immediate access cavity preparation for drainage
- Complete pulp removal and canal irrigation
- Intracanal medication placement (calcium hydroxide)
- Occlusal adjustment to reduce biting pressure
- Pain medication prescription for patient comfort
The emergency dentist focuses on eliminating the bacterial source while providing symptomatic relief. Definitive root canal treatment follows emergency care.
Facial Swelling Assessment
Facial swelling associated with dental infections requires careful evaluation by an emergency dentist on Avenue Road. The location and extent of swelling determine treatment urgency and approach.
Swelling Classification:
- Localized: confined to the immediate tooth area
- Diffuse: spreading to facial spaces
- Severe: involving multiple facial spaces or causing airway compromise
Warning Signs Requiring Hospital Referral:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- High fever with systemic toxicity
- Rapid progression of swelling
- Involvement of deep neck spaces
The emergency dentist monitors these patients closely and coordinates with medical colleagues when necessary.
Emergency Access Cavity Preparation
Proper access cavity preparation by an emergency dentist on Avenue Road allows effective treatment of endodontic emergencies. Correct technique ensures complete access to infected tissue.
Access Cavity Guidelines:
- Location based on pulp chamber anatomy
- Size adequate for complete pulp removal
- Shape following pulp chamber outline
- Depth extending into coronal pulp chamber
- Smooth walls without procedural errors
The emergency dentist uses appropriate bur selection and maintains adequate cooling during preparation. Proper isolation prevents contamination during treatment.
Temporary Restoration Materials
When immediate definitive treatment is not possible, an emergency dentist on Avenue Road places appropriate temporary restorations to protect the access cavity.
Temporary Material Selection:
- Zinc oxide eugenol for sedative properties
- Glass ionomer for fluoride release and adhesion
- Composite resin for aesthetic requirements
- Cavit for easy removal at follow-up
The emergency dentist selects materials based on expected duration and clinical requirements. Proper sealing prevents bacterial recontamination.
Pain Management Strategies
Effective pain control represents a primary goal for an emergency dentist on Avenue Road treating endodontic emergencies. Evidence-based approaches provide optimal patient comfort.
Recommended Pain Management:
- Ibuprofen 400-600mg every 6-8 hours (anti-inflammatory)
- Acetaminophen 500-1000mg every 6 hours (analgesic)
- Combination therapy for enhanced effectiveness
- Prescription analgesics for severe pain (limited duration)
The emergency dentist provides clear instructions for medication use and monitors patient response to treatment.
North Toronto Dental Centre provides comprehensive emergency endodontic services with experienced professionals. Contact them at 416-783-4433 or reception@ntdental.ca when you need an emergency dentist on Avenue Road. You may also contact us to request care.
The clinic is open Monday through Thursday from 8:00am to 6:00pm, Friday and Saturday from 8:00am to 3:00pm (two Saturdays per month), ensuring access to emergency care.
Understanding endodontic emergencies helps patients recognize serious conditions and seek appropriate treatment from qualified dental professionals.
Archive